Bloodaxe: The Next Epic Viking Saga Coming to Prime Video
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Fans of Vikings and Vikings: Valhalla have been hungry for more Norse drama, and now their wait is almost over. Amazon Prime Video has greenlit a brand-new series, Bloodaxe, set to bring one of history’s most notorious Viking rulers to life: Eric Haraldsson, better known as Eric Bloodaxe. From the Creator of Vikings The series comes from none other than Michael Hirst, the creator and writer behind Vikings, joined this time by his son, Horatio Hirst. Together, they promise to deliver a fresh standalone story that will capture the grit, passion, and intrigue of the Viking Age while expanding on the saga-style storytelling fans love. Who Was Eric Bloodaxe? Eric Bloodaxe was the son of Norway’s first king, Harald Fairhair,...

When the Vikings Besieged Paris — Twice!
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.Most people know Vikings raided coastal villages…But did you know they once sailed hundreds of miles inland and laid siege to Paris—twice?The first siege came in 845 AD, when the legendary warrior Ragnar Lothbrok (yes, that Ragnar) led 120 longships up the Seine River with thousands of men. They stormed the city, demanded a ransom, and walked away with over 7,000 pounds of silver. Paris bought its survival—but it wouldn’t be the last time.Fast forward to 885 AD, and the Norse were back—this time in even greater numbers.Up to 30,000 Viking warriors launched a brutal siege that lasted...

What the Winter Solstice Represents
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15. What the Winter Solstice Represents Symbolism: Death and Rebirth: The solstice is often seen as the "death" of the old year and the "birth" of a new cycle. Hope and Renewal: It signifies a turning point, where the darkness begins to recede and the light returns. Astronomical Significance: The Winter Solstice occurs when the Earth's axial tilt is farthest from the Sun in the Northern Hemisphere. It marks the shortest day and longest night of the year. After the solstice, days gradually begin to grow longer, symbolizing the return of light and hope. Origins of Winter...

Before Columbus: Proof of Vikings in North America
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.The primary historic evidence supporting Viking presence in North America around 1000 AD is based on archaeological findings, particularly at the site of L'Anse aux Meadows in Newfoundland, Canada. Here’s a breakdown of the key evidence: 1. L'Anse aux Meadows Site Location: Newfoundland, Canada Description: Excavated in the 1960s, L'Anse aux Meadows is widely accepted as the site of a Viking settlement, dating back to around 1000 AD. Findings: Artifacts: Several artifacts of Norse origin have been found, including: A bronze cloak pin similar to those used by Vikings in Greenland and Iceland. Iron nails and rivets consistent...

Norse Hel versus Christian Hell
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.In Norse mythology, Hel is both a place and a goddess. The goddess Hel, daughter of Loki and the giantess Angrboda, rules over the realm also called Hel (or Helheim) in Niflheim, where many of the dead reside. The term "Hel" itself is cognate with the Old English hell, but Norse Hel and the Christian concept of hell diverge in significant ways. Here are a few points of overlap and distinction: Role and Rulership of the Dead Hel (Norse): Hel is a realm for those who do not die in battle, including those who pass from old age,...

Loki’s Unique Family in Norse Mythology
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.A Saga-Based Exploration: Loki, one of the most fascinating figures in Norse mythology, is often remembered for his cunning, shapeshifting abilities, and unpredictable nature. Yet, what makes him even more compelling is his extraordinary and diverse family. From monstrous creatures to gods, Loki’s offspring play pivotal roles in the mythological events, especially during Ragnarök. Alongside his children, his relationship with his wife Sigyn provides a glimpse into a contrasting side of Loki's chaotic existence. Let’s explore Loki’s unique family, focusing on each child and his wife as depicted in historical sources like The Poetic Edda, The Prose Edda,...

Evidence of Vikings in North America ...before Columbus
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15. The tale of Norse exploration in North America, long relegated to the realm of legend and myth, has increasingly come under scrutiny from historians and archaeologists. For decades, evidence has been mounting that the Vikings, under the leadership of Leif Erikson and his peers, did indeed reach the shores of what is now Canada long before Christopher Columbus set sail (as seen in this painting from 1893).In this blog post, we’ll explore the compelling evidence supporting this claim and consider the reasons behind the Vikings' departure from these lands. The Evidence of Viking Presence Vinland: The Historical...

Vikings (Rus) and their impact on Ukraine and Russia
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.While we fully support Ukraine's independence (and have friends who live there), it is interesting to note that there is a lot of evidence that Russia's origins are directly connected to Ukraine, as well as connections to the Swedish Vikings that once ruled areas of Ukraine. Russian President Vladimir Putin (on this subject) once stated, "Kiev is the mother of all Russian cities." The connection between the word "Russia" and the Rus of Kyiv in Ukraine is a topic steeped in (Swedish) Viking history, cultural evolution, and political significance. To understand whether there is a direct connection between these two terms,...

Does Russia have Swedish Viking roots?
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.There is no doubt that Swedish Vikings, known as the Rus of Kiev, once ruled the area now known as Ukraine. But there is also a theory that the original Russian royal family (particularly the Rurikid dynasty) was of Swedish Viking heritage. This theory is supported by a combination of historical texts, archaeological findings, and linguistic evidence. Several primary and secondary sources provide information on the Scandinavian roots of the Rurikid dynasty, and they contribute to the argument that the first Russian rulers were of Norse (and specifically Swedish) origin. Below are some of the key historic sources and evidence:...
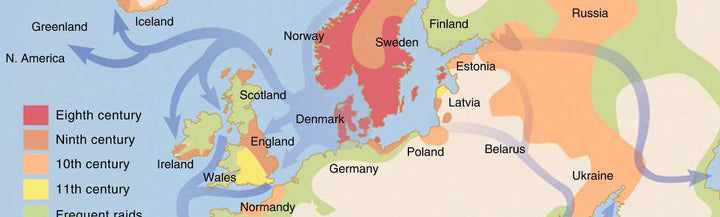
Where Do Vikings Come From?
Posted by Sons Of Vikings on
Thanks for visiting our blog! As a thank-you, enjoy 15% off your first order in our online Viking Shop with the discount code BLOG15.When we think of Vikings, images of fierce warriors, longships cutting through misty waters, and horned helmets (a myth, by the way) often come to mind. But where did these seafaring people originate? The Vikings hail from Scandinavia, a region in Northern Europe that includes modern-day Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. Their story is one of exploration, trade, conquest, and cultural influence that has left a lasting impact on the world. The Scandinavian Homeland The Vikings emerged from the Scandinavian Peninsula around the late 8th century. This region, characterized by its rugged terrain, fjords, and harsh climate, shaped the...